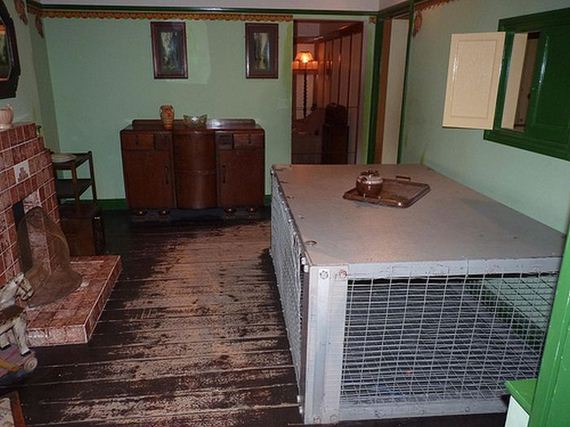

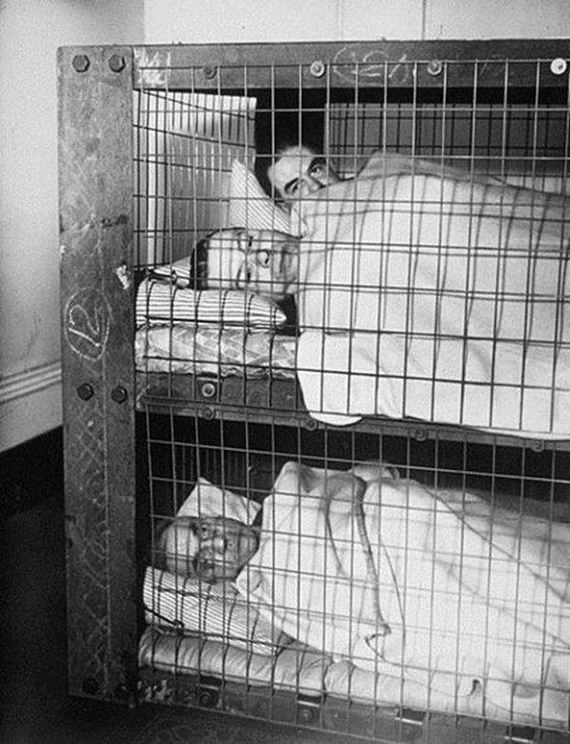
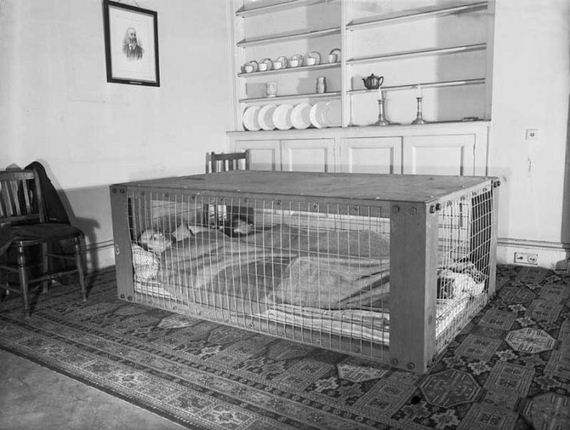
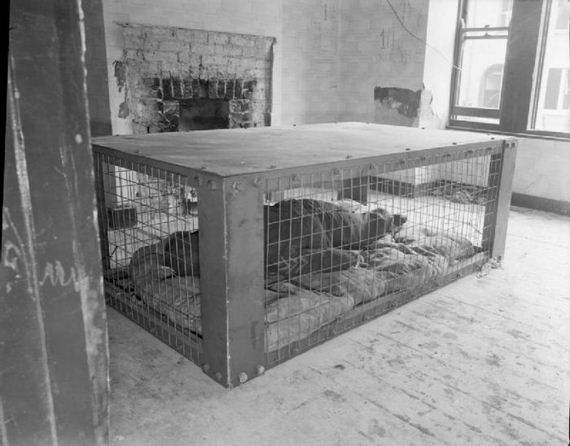
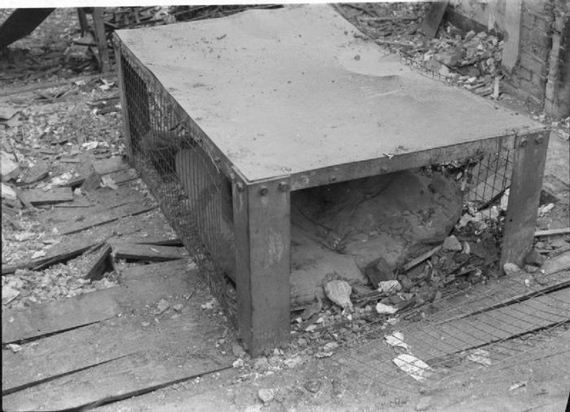
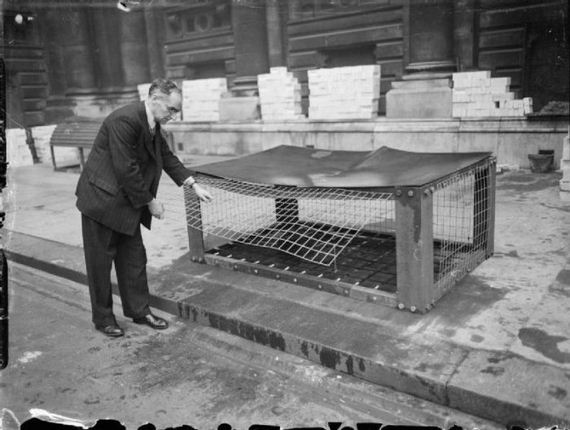
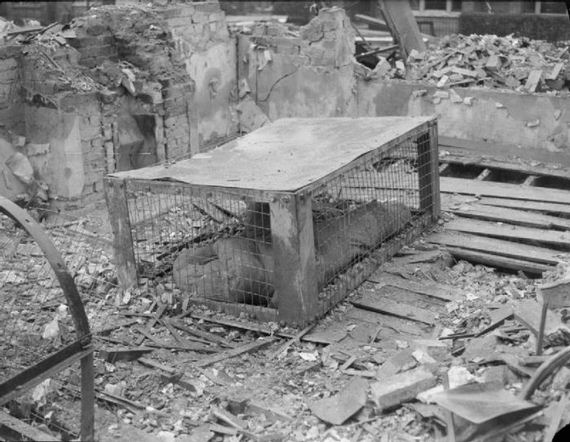
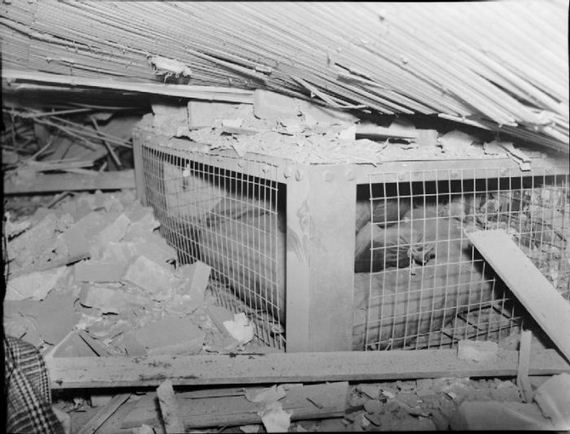
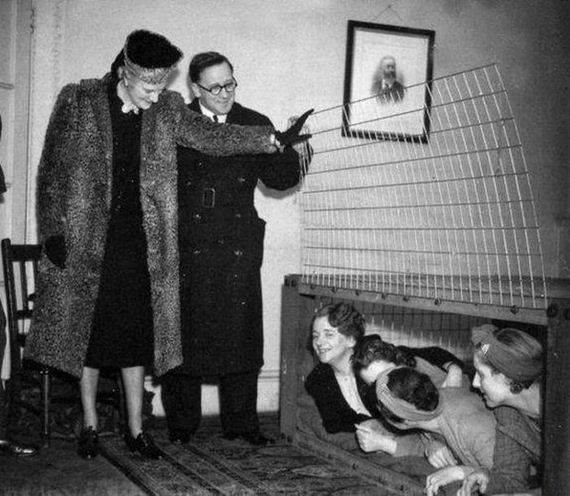
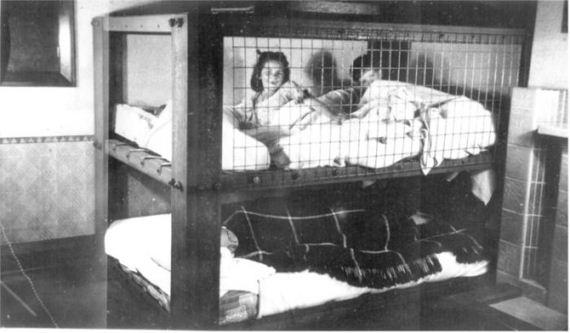
The Morrison shelter were indoor shelters with a cage-like construction beneath it. It was designed by John Baker and named after Herbert Morrison, the Minister of Home Security at the time. It was the result of the realization that due to the lack of house cellars it was necessary to develop an effective type of indoor shelter. The shelters came in assembly kits, to be bolted together inside the home. They were approximately 6 ft 6 in (2 m) long, 4 ft (1.2 m) wide and 2 ft 6 in (0.75 m) high, had a solid 1/8 in (3 mm) steel plate “table” top, welded wire mesh sides, and a metal lath “mattress”- type floor. The shelter was provided free to households whose combined income was less than £400 per year. 500,000 Morrison shelters had been distributed by the end of 1941, with a further 100,000 being added in 1943 to prepare the population for the expected German V-1 flying bomb (doodlebug) attacks.









 Barnorama All Fun In The Barn
Barnorama All Fun In The Barn